


Wide flange beam are structural components that are used in the Structural Industry mostly in Solar Structures, Construction Industry to support buildings and bridges. They are also known as W-Beam. The shape of these beams resembles the letter “W,” with two parallel flanges that are connected by a central web. The flanges are wider than the web, hence the name wide flange beam.
Wide flange beam are made from a variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, and other alloys. Steel beams are the most commonly used because they are strong, durable, and cost-effective.
Wide flange beam are typically used in horizontal & vertical applications, such as Solar Panels, Building Homes, Freeways, Overpasses, and Commercial Buildings. They are designed to resist bending and deflection, which makes them ideal for applications that require high strength and durability.
Industries use W-beam throughout Industrial Projects to build a wide array of different commercial, residential, and municipal structures. Creating stronger Industrial Structures, commercial buildings, including skyscrapers or buildings with unique architectural designs.
Some of the most common uses include:
Builders use W-beams throughout the construction industry to build a wide array of different residential, commercial, and municipal structures. Creating stronger commercial buildings, including skyscrapers or buildings with unique architectural designs.
Some of the most common uses include:
Strength and Stability: Wide flange beam is renowned for their superior load-bearing capacity and structural integrity. Their unique cross-sectional shape, characterized by a wider flange and narrower web, allows it to efficiently distribute weight and resist bending and deflection. This inherent strength ensures the stability and longevity of structures in various applications.
Wide Range of Sizes: Wide flange beam come in a broad range of sizes, allowing for flexibility in design and meeting specific project requirements. From smaller residential applications to large-scale industrial projects, there is a wide flange beam size available to accommodate various structural needs.
Structural Versatility: Wide flange beam is incredibly versatile, making it suitable for a diverse array of construction projects. They are commonly used as horizontal supports in building frames, as columns for vertical support, and as headers and beams in floor and roof systems. Their adaptability allows for innovative designs and efficient use of space.
Ease of Integration: Wide flange beam seamlessly integrate with other structural components, enabling efficient connections and assembly. They can be easily welded, bolted, or spliced to create robust and reliable connections, facilitating the construction process and ensuring structural integrity.
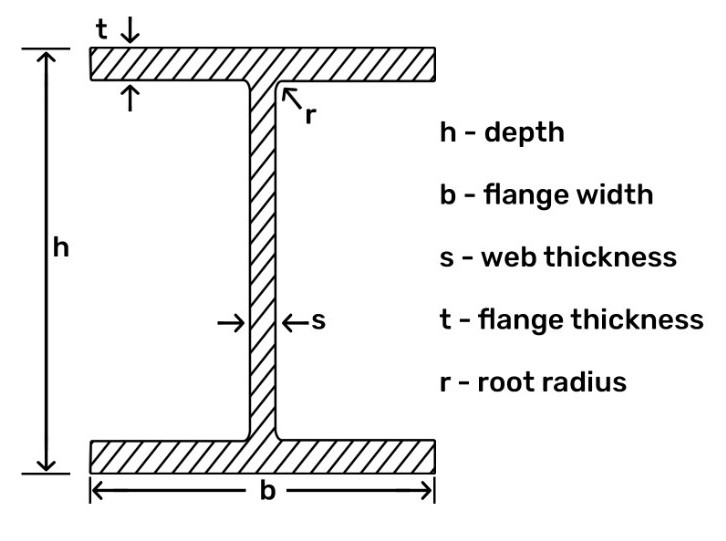
To best meet the needs of different construction projects that have to accommodate a wide range of weights, W-beam steel mills produce multiple different types of W-beams with different dimensions, material options, and reinforcement elements. The dimensions of a given W-beam largely determine the amount of weight the beam can support. There are four key dimensions of W-beams to account for:
Once you determine your dimensions based on the requirements of your specific construction project (including both linear requirements and weight-bearing requirements), you can shop for the right W-beams by using steel service center catalogues and engineering guides to find the specific W-beam with your specific dimensions. The American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) can guide you through the standardized beam sizes. This allows engineers, architects, and builders to communicate easily across industries and coordinate orders with minimal risk of error.
This measurement is the entire height of the beam, from the outer surface of the top flange to the outer surface of the bottom flange.
This dimension establishes the width of the flange, from the left to the right of its cross-section. W-beam flanges have the same width.
This is the thickness of the flange from the top surface to the bottom surface. The left and right sides of both flanges should have the same thickness.
The “web” refers to the vertical stem or main body of the beam. This dimension is the thickness across the web from left to right.
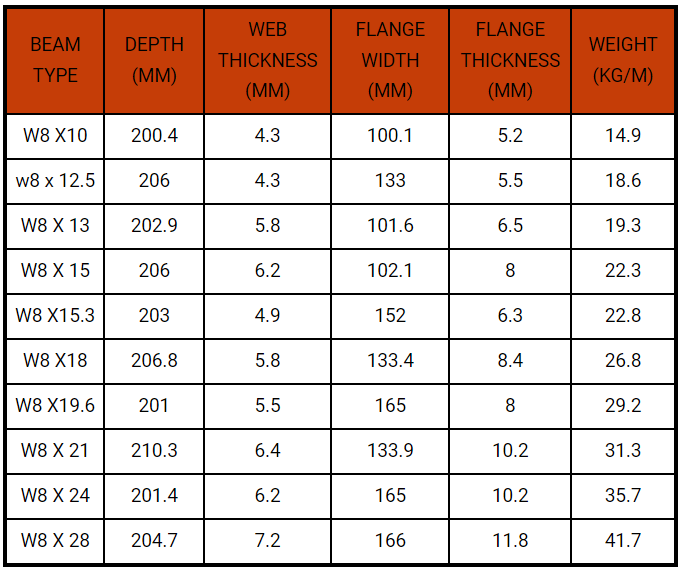
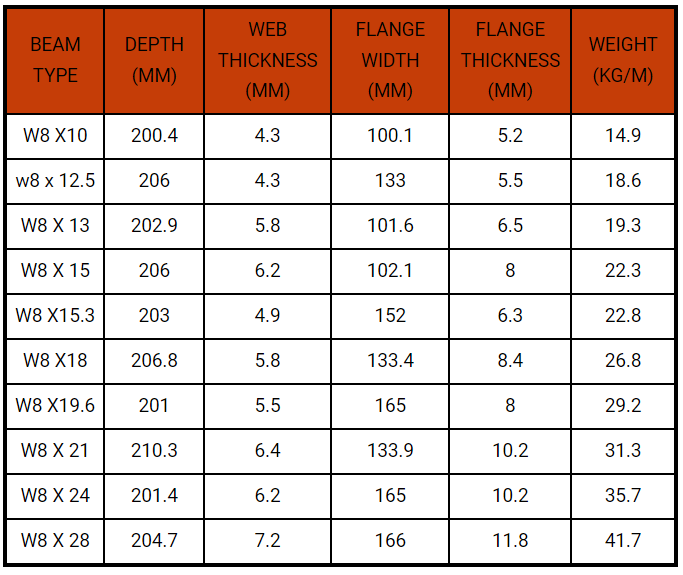
| BEAM TYPE | DEPTH (MM) | WEB THICKNESS (MM) | FLANGE WIDTH (MM) | FLANGE THICKNESS (MM) | WEIGHT (KG/M) |
| W6 X 7 | 147.1 | 3.4 | 99.2 | 4.1 | 10.4 |
| W6 X 7.75 | 147.8 | 3.8 | 99.6 | 4.5 | 11.18 |
| W6 X 8.5 | 148.1 | 4.3 | 100.1 | 5 | 12.6 |
| W6 X 9 | 149.9 | 4.3 | 100.1 | 5.5 | 13.4 |
| W6 X 10.4 | 151.4 | 5.1 | 100.8 | 6.3 | 15.5 |
| W6 X 12 | 153.2 | 5.8 | 101.6 | 7.1 | 17.9 |
| W6 x 12.1 | 151.9 | 5.1 | 140 .0 | 5.6 | 18 |
| W6 X 15 | 152.1 | 5.8 | 152.1 | 6.6 | 22.3 |
| W6 X 16 | 159.5 | 6.6 | 102.4 | 10.3 | 23.8 |
| W6 X 20 | 157.5 | 6.6 | 152.9 | 9.3 | 29.8 |
| W6 X 25 | 162.1 | 8.1 | 154.4 | 11.6 | 37.2 |
| BEAM TYPE | DEPTH (MM) | WEB THICKNESS (MM) | FLANGE WIDTH (MM) | FLANGE THICKNESS (MM) | WEIGHT (KG/M) |
| W8 X 10 | 200.4 | 4.3 | 100.1 | 5.2 | 14.9 |
| W8 x 12.5 | 206 | 4.3 | 133 | 5.5 | 18.6 |
| W8 X 13 | 202.9 | 5.8 | 101.6 | 6.5 | 19.3 |
| W8 X 15 | 206 | 6.2 | 102.1 | 8 | 22.3 |
| W8 X 15.3 | 203 | 4.9 | 152 | 6.3 | 22.8 |
| W8 X 18 | 206.8 | 5.8 | 133.4 | 8.4 | 26.8 |
| W8 X 18 | 206.8 | 5.8 | 133.4 | 8.4 | 26.8 |
| W8 X 19.6 | 201 | 5.5 | 165 | 8 | 29.2 |
| W8 X 21 | 210.3 | 6.4 | 133.9 | 10.2 | 31.3 |
| W8 X 24 | 201.4 | 6.2 | 165 | 10.2 | 35.7 |
| W8 X 28 | 204.7 | 7.2 | 166 | 11.8 | 41.7 |

copyright@2024 YAxis Structural Steel. Designed & Developed by Websoft Techno
WhatsApp us
